Introduction
JavaScript is a programming language that is primarily used for front-end web development. It is often used alongside HTML and CSS to create interactive and dynamic web pages. Here are some common uses of JavaScript:- Adding interactivity to web pages: JavaScript allows developers to add interactive elements to web pages, such as buttons, pop-up boxes, and menus.
- Creating web-based games: JavaScript can be used to create simple games that run in a web browser.
- Building web applications: JavaScript is used to create web applications, such as online calculators, chat applications, and collaborative editing tools.
- Developing browser extensions and add-ons: JavaScript is used to create extensions and add-ons for web browsers, which can enhance the functionality of the browser.
- Creating server-side applications: JavaScript can be used to create server-side applications, such as APIs and web servers.
Why do we learn javascript?
JavaScript is a high-level programming language that is primarily used for front-end web development. It is often used alongside HTML and CSS to create interactive and dynamic web pages. Here are some examples of what you can do with JavaScript:
- Form validation: JavaScript can be used to validate form inputs to ensure that they meet certain criteria, such as being a valid email address or a certain length.
- DOM manipulation: JavaScript can be used to manipulate the Document Object Model (DOM) of a web page, allowing you to add, remove, or modify HTML elements dynamically.
- Event handling: JavaScript can be used to handle user events, such as clicks, mouse movements, and key presses, and respond to them in real-time.
- Animation: JavaScript can be used to create animations on web pages, such as fading in and out, sliding, and rotating elements.
- API integration: JavaScript can be used to integrate with external APIs, such as social media platforms, weather services, and payment gateways, to retrieve and display data on a web page.
- Browser detection: JavaScript can be used to detect the user's browser and adjust the functionality of the web page accordingly.
- Game development: JavaScript can be used to create simple games that run in a web browser, such as Snake or Tetris.
History of javascript?
JavaScript quickly became popular because it allowed web developers to add interactivity and dynamic content to their web pages, which was previously not possible with static HTML. It was standardized as ECMAScript in 1997, and subsequent versions of JavaScript have been based on this standard.
Over the years, JavaScript has evolved to become a powerful and versatile programming language, capable of running on both the client side (in a web browser) and the server side (using Node.js). It is now one of the most widely used programming languages in the world, with a large and active community of developers constantly creating new libraries, frameworks, and tools to enhance its capabilities.
- Variables: Variables are used to store data in JavaScript. You can declare a variable using the "var" keyword. Here's an example:
- Functions: Code blocks known as functions carry out a certain duty. Using the "function" keyword, a function can be defined.
Here's an example:
- Conditional statements: Conditional statements allow you to execute code based on a condition. You can use the "if", "else if", and "else" keywords to create conditional statements. Here's an example:
- Loops: Loops allow you to repeat a block of code a certain number of times. You can use the "for" loop, "while" loop, or "do-while" loop in JavaScript. Here's an example using a "for" loop:
- Arrays: Arrays are used to store multiple values in a single variable. You can create an array using square brackets and separate the values with commas. Here's an example:
In this example, "name" is the variable name, and "John" is the value assigned to the variable. The "var" keyword is used to declare the variable.
This will display a dialog box asking the user to enter their name, and then store the entered value in the "name" variable.
Variables can also be updated with new values as needed. For example, you could update the value of the "name" variable like this:
This would change the value of the "name" variable from "John" to "Sarah".
In JavaScript, variables are dynamically typed, which means that you don't need to specify the data type when declaring a variable. The data type is automatically determined based on the value assigned to the variable.
Here are some examples of other types of data that can be stored in variables:
In this example, the function is named "sayHello" and it uses the "console.log" method to print the message "Hello, world!" to the console. To call the function and execute its code, you would simply write:
This would invoke the "sayHello" function and cause it to print the message to the console.
Functions can also accept parameters, which are values that are passed into the function to be used in its code. Here is an example of a function that accepts a parameter:
In this example, the "greet" function accepts a parameter called "name". When the function is called, a value for the "name" parameter must be passed in, like this:
This would cause the function to print the message "Hello, John!" to the console.
In this example, the "square" function accepts a parameter called "x" and returns the result of multiplying it by itself. To use the function and get its return value, you would write:
This would compute the square of 5 (which is 25) and store the result in the "result" variable, which is then printed to the console.
These are just a few examples of how functions can be used in JavaScript. As you become more familiar with the language, you'll learn many other ways to use functions to organize and simplify your code.
In this example, the code inside the "if" statement will only be executed if the "age" variable is greater than or equal to 18. If the condition is true, the message "You are an adult." will be printed on the console.
If-Else Statement
The "if-else" statement is used to execute one block of code if a certain condition is true, and a different block of code if the condition is false. Here is an example:
In this example, the code inside the "if" statement will be executed if the "grade" variable is greater than or equal to 90. If it is not, the code inside the first "else-if" statement will be executed if "grade" is between 80 and 89, and so on. If none of the conditions are true, the code inside the "else" statement will be executed. In this case, since "grade" is 75, the message "C" will be printed to the console.
There are many reasons why you might use conditional statements in JavaScript. Here are some examples:
2. Decision-Making: You can use conditional statements to make decisions in your code. For example, you might want to display a different message to a user depending on whether they are logged in or not.
3. Looping: Conditional statements can be used to control loops. For example, you might want to stop a loop from executing when a certain condition is met.
4. Event Handling: You can use conditional statements to handle events in your code. For example, you might want to display a message when a button is clicked, but only if certain conditions are met.
The "for" loop is used to execute a block of code a specified number of times. Here is an example:
In this example, the loop will execute 5 times, starting with i=0 and increasing by 1 each time until i=4. The message "The value of i is x" will be printed to the console each time the loop executes.
The "while" loop is used to execute a block of code as long as a certain condition is true. Here is an example:
In this example, the loop will execute as long as i is less than 5. The message "The value of i is x" will be printed to the console each time the loop executes, and i will be incremented by 1 each time.
Do-While Loop
The "do-while" loop is similar to the "while" loop, but it will always execute the code block at least once, even if the condition is false. Here is an example:
In this example, the code block will be executed once even though i is initially 0. After that, the loop will continue to execute as long as i is less than 5.
These are just a few examples of how loops can be used in JavaScript. As you become more familiar with the language, you'll learn many other ways to use loops to execute code repeatedly and automate tasks in your programs.
loops are an important tool in JavaScript because they allow you to write more efficient and effective code. They can save you time by allowing you to automate repetitive tasks, and they can help you avoid writing repetitive code by allowing you to iterate over arrays and perform the same operation on each element. some reasons why we use/learn loops in javascript iterating over Arrays, Data Validation, Creating Patterns, and Automating Tasks, if you want to learn about this follow Guerillateck.
In this example, the array "myArray" contains five values, which are the numbers 1 through 5. You can access individual values in an array by using their index number, which starts at 0. Here is an example:
In this example, the first console.log statement accesses the first value in the array (which has an index of 0) and outputs it to the console. The second console.log statement accesses the third value in the array (which has an index of 2) and outputs it to the console.
You can also modify the values in an array by assigning new values to their index numbers. Here is an example:
In this example, the first value in the array (which was originally 1) is changed to 10 by assigning a new value to its index number.
In this example, a "for" loop is used to iterate over each element in the array and output it to the console. The "length" property of the array is used to determine the number of elements in the array, so the loop will execute once for each element.
Overall, arrays are an important data structure in JavaScript because they allow you to store multiple values in a single variable and perform operations on them efficiently using loops and other techniques.
- push(): The push() method adds one or more elements to the end of an array. Here's an example:
In this example, the push() method is used to add the value 4 to the end of the array "myArray".
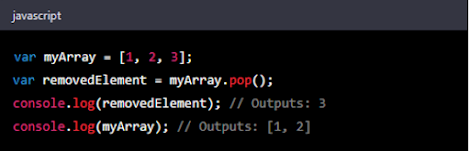
- pop(): The pop() method removes the last element from an array and returns it. Here's an example:
- shift(): The shift() method removes the first element from an array and returns it. Here's an example:
- unshift(): The unshift() method adds one or more elements to the beginning of an array. Here's an example: