COMPUTER NETWORKING FOR CCNA BEGINNERS
TWO TYPES OF TECHNOLOGIES USED IN NETWORKING
- -WIRED
- -WIRELESS
To construct a high-speed local area network, ITU-T G.hn technology takes advantage of the coaxial cable, phone, and power lines that already exist in homes.
Standard wired Ethernet and other protocols use twisted pair cabling. 4 pairs of copper wiring, which can be used for both voice and data transmission, make up the standard configuration. Crosstalk and electromagnetic induction are diminished by using two wires that have been twisted together. 2 Mbit/s to 10 Gbit/s are the available transmission speeds. Unshielded and shielded twisted pairs (UTP and STP, respectively) are the two variations of twisted pair cabling. There are multiple category ratings for each form, each of which is intended for use in a different situation.
Glass fiber is an optical fiber. Through the use of lasers and optical amplifiers, it transmits light pulses that stand in for data. Optical fibers have a very low transmission loss and are immune to electrical interference, which are some benefits over metal cables. Using dense wave division multiplexing, optical fibers may send data at up to billions of bits per second by concurrently transmitting numerous streams of information on various light wavelengths. Optic fibers are utilized in undersea communication cables that connect continents and can be used for lengthy cable runs carrying extremely high data rates. A single-mode optical fiber (SMF) and multi-mode optical fiber (MMF) are the two fundamental varieties of fiber optics. The benefit of using single-mode fiber is that it can maintain a coherent signal for dozens or even 100 km. Depending on the data rate and cable grade, multimode fiber can only be extended for a few hundred or perhaps a few dozen of meters, making it more expensive to terminate.
Network connections can be established wirelessly using radio or other electromagnetic means of communication.
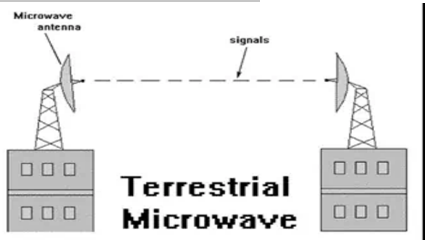
Terrestrial microwave — Terrestrial microwave communication makes use of satellite-dish-like transmitters and receivers that are situated on Earth. All communications are restricted to line-of-sight because terrestrial microwaves operate in the low gigahertz band. There are roughly 40 miles (64 km) between relay stations.
The radio communications technology used by cellular networks is diverse. The systems separate the covered region into several different geographic regions. A low-power transceiver provides service to each location.
Technologies involving radio and spread spectrum - Wireless LANs use high-frequency radio technology akin to digital cellular. To allow communication between numerous devices in a constrained space, wireless LANs use spread spectrum technology. Wi-Fi is an open-standards wireless radio-wave technology that is commonly used. IEEE 802.11 defines Wi-Fi.
The Interplanetary Internet IP via Avian Carriers was a lighthearted Request for Comments that was published as RFC 1149, extending the Internet to extraterrestrial dimensions using radio waves and optical techniques. In 2001, it was put into practice in real life.
Network nodes (node networking)
A network interface controller (NIC) is a piece of hardware for computers that links them to network media and can process basic network data. The NIC, for instance, might comprise circuitry and a connector for receiving a cable or an antenna for wireless transmission and reception.
Each NIC in Ethernet networks has its own Media Access Control (MAC) address, which is often kept in the controller's permanent memory. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) upholds and regulates MAC address uniqueness to prevent address conflicts between network devices. Ethernet MAC addresses have a six-octet size limit. To identify NIC manufacturers, the three most important octets are set aside. Every Ethernet interface made by these manufacturers has its three least-significant octets assigned in a unique way utilizing just the prefixes that have been given to them.
Repeaters recreate the signal quickly, although they still operate on the physical layer of the OSI model. This may damage the performance of the network and its ability to function properly by causing a propagation delay. As a result, many network topologies, such as the Ethernet 5-4-3 rule, have a cap on the number of repeaters that can be utilized in a network.
The term "Ethernet hub" refers to an Ethernet repeater with several ports. A repeater hub helps the network with collision detection and fault isolation in addition to reconditioning and disseminating network signals. Modern network switches have rendered hubs and repeaters in LANs completely obsolete.
Bridges and switches
To create a single local network out of two or more network segments, bridges and switches operate at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model. Both are devices that forward data frames across ports based on each frame's destination MAC address. By looking at the source addresses of incoming frames, they can determine how physical ports and MAC addresses are related, and they only forward frames when necessary. When attempting to communicate with an unidentified destination MAC, the device broadcasts the request to all ports other than the source and deduces the location from the response.
Bridges and switches divide the network's collision domain
but maintain a single broadcast domain. Network segmentation through bridging
and switching helps break down a large, congested network into an aggregation of
smaller, more efficient networks.
Bridges and switches separate the network's broadcast domain while keeping its collision domain intact. A large, crowded network can be divided into a collection of smaller, more effective networks using network segmentation techniques like bridging and switching.
A typical home or small office router shows the ADSL telephone line and Ethernet network cable connections
A firewall is a piece of network hardware or software that regulates access restrictions and network security. Connections between potentially insecure external networks, such as the Internet, and secure internal networks are protected by firewalls. Firewalls are often set up to allow actions from recognized sources while rejecting requests for access from unrecognized ones. Firewalls are becoming increasingly important for network security as cyberattacks continue to rise.
COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS
There are many different types of communication protocols, each designed for specific purposes and applications. Some common communication protocols include:
2)HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP): This is the protocol used for transferring data on the World Wide Web. It specifies how web browsers and servers should interact with each other.
3)File Transfer Protocol (FTP): This protocol is used for transferring files over a network. It allows users to upload and download files from remote servers.
4)Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP): This is the protocol used for sending and receiving email messages.
5)Hypertext Markup Language (HTML): This is a markup language used for creating web pages. It defines the structure and content of web pages.
6)Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS): These protocols are used for secure data transmission over a network. They provide encryption and authentication to ensure that data is transmitted securely.
GEOGRAPHICAL SCALE
Geographic scale refers to the spatial extent of a geographical phenomenon or process. It is a way of categorizing the size or scope of a phenomenon or process about its spatial context. There are several different scales of geography, each with its own characteristics and scope.
ORGANIZATIONAL SCOPE
In most cases, the companies who control a network administer it. Intranets and extranets may be combined in private enterprise networks. The Internet, which has no single owner and enables nearly infinite worldwide connectivity, may likewise be made available via their network.
2. Web-based interface: An intranet typically uses a web-based interface to allow users to access and share information.
3. Secure access: Access to an intranet is restricted to authorized users, and it typically requires a username and password to log in.
4. Centralized content management: An intranet is typically managed by a central team or department within the organization, which is responsible for managing the content and ensuring that it is up to date.
5. Collaboration tools: An intranet typically includes tools for collaboration and communication, such as email, instant messaging, and discussion forums.
6. Search functionality: An intranet typically includes a search function that allows users to quickly find the information they need.
2. Web-based interface: An extranet typically uses a web-based interface to allow external users to access and share information.
3. Collaborative features: An extranet may include collaborative features such as email, instant messaging, discussion forums, and file sharing, which allow external users to communicate and work with internal staff.
4. Centralized content management: An extranet is typically managed by a central team or department within the organization, which is responsible for managing the content and ensuring that it is up to date.
5. Integration with internal systems: An extranet may be integrated with the organization's internal systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM) or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, to provide external users with access to relevant information.
2. Standard communication protocols: The Internet uses a standard set of communication protocols, such as TCP/IP, HTTP, and SMTP, to ensure that devices can communicate with each other regardless of their hardware or software.
3. Open architecture: The Internet is built on an open architecture that allows anyone to create and publish content, applications, and services, and make them available to anyone else on the network.
4. Search functionality: The Internet includes a search function that allows users to find information on any topic quickly and easily.
5. Social networking: The Internet includes a variety of social networking platforms that allow users to connect and interact with each other online.
6. E-commerce: The Internet has become a major platform for e-commerce, allowing businesses to sell goods and services to customers all over the world.
7. Multimedia content: The Internet includes a vast array of multimedia content, including text, images, audio, and video, that can be accessed and shared by anyone with an Internet connection.
Partial map of the Internet based on 2005 data. Each line is drawn between two nodes, representing two IP addresses. The length of the lines indicates the delay between those two nodes.
The Darknet, also known as the Dark Web, is a portion of the Internet that is not indexed by traditional search engines and can only be accessed using specialized software or configurations. It is a network that is intentionally hidden and difficult to access and is often associated with illegal activities.
2. Encryption: The Darknet uses encryption to ensure that communication and transactions remain secure and private.
3. Specialized software: Accessing the Darknet requires specialized software, such as Tor (The Onion Router) or I2P (Invisible Internet Project), which enable users to browse the web anonymously and access hidden websites.
4. Hidden websites: The Darknet includes hidden websites that are not accessible through traditional search engines, and often require specific URLs or access codes to enter.
5. Illegal activities: The Darknet has gained notoriety for its association with illegal activities, such as the sale of drugs, weapons, and stolen data, as well as for hosting illegal marketplaces, forums, and communities.
so that's it for today guys, follow us to learn more.....
happy learning.....













No comments:
Post a Comment